在打开文件、列举文件或者stat()操作时,用户端给的是文件路径信息,内核文件系统需要根据路径,查找到对应的inode,这样才能生成file对象,才能进行后续的读写等操作。所以,文件查找是一个基础能力,是其他文件操作的前置条件。
所谓查找文件,就是找到路径对应的dentry项,通过dentry项找到对应inode信息,有了inode才能对文件进行其他操作。文件查找时,优先在dcache缓存中查找,如果没有找到,需要到磁盘上进行遍历。
在dcache中查找,是VFS层面的基本动作,dcache如果没有找到,VFS就会调用具体文件系统的lookup()函数,到磁盘上进行遍历。以ext2文件系统为例,lookup具体流程如下:
- ① 根据父目录inode、当前文件名,查找对应的目录项,最终查找到对应的ino(ext2_inode_by_name)
- ② 根据ino,从磁盘上读取inode信息(ext2_iget)
- ③ 连接dentry和inode,处理目录项的别名(d_splice_alias)

// ext2/namei.c
static struct dentry *ext2_lookup(struct inode * dir, struct dentry *dentry, unsigned int flags)
{
struct inode * inode;
ino_t ino;
int res;
if (dentry->d_name.len > EXT2_NAME_LEN)
return ERR_PTR(-ENAMETOOLONG);
res = ext2_inode_by_name(dir, &dentry->d_name, &ino); // ①
if (res) {
if (res != -ENOENT)
return ERR_PTR(res);
inode = NULL;
} else {
inode = ext2_iget(dir->i_sb, ino); // ②
if (inode == ERR_PTR(-ESTALE)) {
ext2_error(dir->i_sb, __func__,
"deleted inode referenced: %lu",
(unsigned long) ino);
return ERR_PTR(-EIO);
}
}
return d_splice_alias(inode, dentry); // ③
}一、前置流程(dcache查找)
以下代码是lookup()的前置流程函数,这个函数会在路径分量处理时调用,VFS先会从dcache中寻找dentry,如果可以找到直接返回;如果找不到,将会调用文件系统的lookup函数查找。
/*
* Parent directory has inode locked exclusive. This is one
* and only case when ->lookup() gets called on non in-lookup
* dentries - as the matter of fact, this only gets called
* when directory is guaranteed to have no in-lookup children
* at all.
*/
static struct dentry *__lookup_hash(const struct qstr *name,
struct dentry *base, unsigned int flags)
{
struct dentry *dentry = lookup_dcache(name, base, flags);
struct dentry *old;
struct inode *dir = base->d_inode;
if (dentry)
return dentry;
......
dentry = d_alloc(base, name);
if (unlikely(!dentry))
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
old = dir->i_op->lookup(dir, dentry, flags);
if (unlikely(old)) {
dput(dentry);
dentry = old;
}
return dentry;
}dcache的查找dentry流程非常简单:比较hash值、比较父dentry、比较文件名,如果都相等,就返回当前dentry。
// dcache.c
/* dentry hash table */
static struct hlist_bl_head *dentry_hashtable __read_mostly;
struct dentry *__d_lookup(const struct dentry *parent, const struct qstr *name)
{
.....
rcu_read_lock();
hlist_bl_for_each_entry_rcu(dentry, node, b, d_hash) {
if (dentry->d_name.hash != hash)
continue;
spin_lock(&dentry->d_lock);
if (dentry->d_parent != parent)
goto next;
if (d_unhashed(dentry))
goto next;
if (!d_same_name(dentry, parent, name))
goto next;
dentry->d_lockref.count++;
found = dentry;
spin_unlock(&dentry->d_lock);
break;
next:
spin_unlock(&dentry->d_lock);
}
rcu_read_unlock();
return found;
}二、根据文件名查询磁盘目录项
如果在缓存中没有命中dentry,那么就需要从磁盘上查找。在磁盘上查找目录项这个过程,和创建目录项的过程类似(见上一期创建目录、上上期创建文件)。通过父目录的缓存page页,逐个页面循环,在单个页面框定struct ext2_dir_entry_2结构,然后比对文件名,详细的流程如下:
- ① 根据父目录的dir->i_size字段,计算出所有页缓存page页面数
- ② 获取目录的起始页(ei->i_dir_start_lookup)
- ③ 从起始页开始循环,挨个地址框住成struct ext2_dir_entry_2,然后检查名称是否相同,如果名称相同,记录page和page_addr,记录当前页面顺序,然后返回dentry项。
- ④ 如果不相同,继续在页面内比对下一条记录
- ⑤ 如果页面内没有,继续看下一个页面
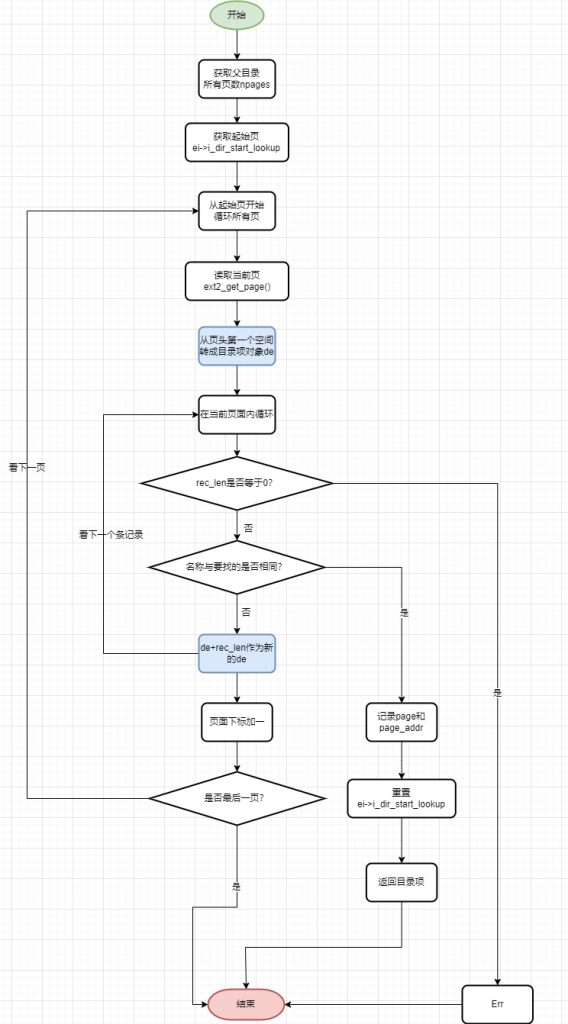
文件名:namei.c,函数:ext2_find_entry()
通过这一个步骤目录项查找,这样就能获取到了ino,为后面获取inode做好了准备。
三、根据ino获取inode(VFS)
上面已经获取到了ino,接下来就是要根据ino获取inode,调用的函数就是ext2_iget()。具体的流程如下:
- ① 从inode哈希表中,根据sb和ino查找vfs的inode,如果找到直接返回(iget_locked)
- ② 如果哈希表中没有inode,说明磁盘的inode还没有加载,那么需要分配一个新inode(vfs和缓存),分配流程最终会调用ext2_alloc_inode进行分配。(iget_locked)
- ③ 如果是新的inode,就要读取磁盘的ext2_inode,然后填充inode信息(ext2_get_inode)
- ③ 填充VFS和缓存inode,包括基本信息、操作表等
- ④ 返回inode
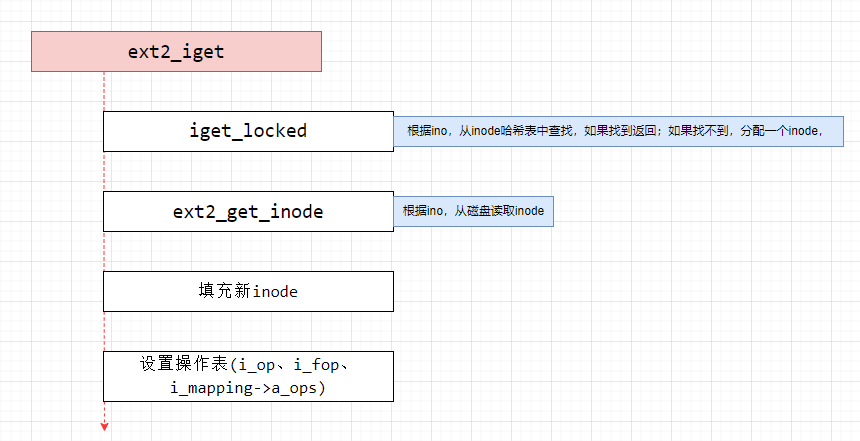
1.查找inode、分配inode(iget_locked)
1)查找inode
从全局哈希表inode_hashtable查询inode,查询开始的偏移量通过hash(sb, ino)计算得到,然后调用函数还是循环比对查找。
2)分配inode
如果全局哈希表中没有查询到,将会通过alloc_inode()新分配一个inode,alloc_inode()函数调用的是super_block的操作表中,注册的alloc_inode()函数指针,最终调用的是ext2_alloc_inode()。
struct inode *iget_locked(struct super_block *sb, unsigned long ino)
{
struct hlist_head *head = inode_hashtable + hash(sb, ino);
struct inode *inode;
again:
spin_lock(&inode_hash_lock);
inode = find_inode_fast(sb, head, ino);
spin_unlock(&inode_hash_lock);
if (inode) {
......
return inode;
}
inode = alloc_inode(sb);
if (inode) {
......
wait_on_inode(inode);
if (unlikely(inode_unhashed(inode))) {
iput(inode);
goto again;
}
}
return inode;
}2.从磁盘读取inode(填充空内存inode用)
如果再hash表中没有找到inode,那么将会新分配一个inode,此时新分配的inode是空的,需要读取磁盘的inode,然后填充数据到,内存inode和VFS的inode。从磁盘读取inode过程非常清晰,具体的流程和代码如下:
- 计算inode所在的块组block_group
- 根据块组信息获取块组描述符gdb
- 计算inode在inode_table的偏移量offset,以及inode所属的块
- 使用sb_bread()读取相应块,得到内存缓冲区
- 缓冲区地址加上偏移量就是对应的inode
// inode.c
static struct ext2_inode *ext2_get_inode(struct super_block *sb, ino_t ino,
struct buffer_head **p)
{
......
block_group = (ino - 1) / EXT2_INODES_PER_GROUP(sb);
gdp = ext2_get_group_desc(sb, block_group, NULL);
if (!gdp)
goto Egdp;
/*
* Figure out the offset within the block group inode table
*/
offset = ((ino - 1) % EXT2_INODES_PER_GROUP(sb)) * EXT2_INODE_SIZE(sb);
block = le32_to_cpu(gdp->bg_inode_table) +
(offset >> EXT2_BLOCK_SIZE_BITS(sb));
if (!(bh = sb_bread(sb, block)))
goto Eio;
*p = bh;
offset &= (EXT2_BLOCK_SIZE(sb) - 1);
return (struct ext2_inode *) (bh->b_data + offset);
......
}3.填充内存inode和VFS的inode
这部分逻辑比较简单,想了解的直接参考代码inode.c的ext2_iget()函数。
四、连接dentry和inode
经过以上二、三两步,已经获取了inode了,dentry在前置流程已经准备成功,接下来连接dentry和inode,这样lookup()的流程就结束了。
// namei.c ext2_lookup()
d_splice_alias(inode, dentry);官方文档:VFS

《07 ext2文件系统IO流程:文件查找lookup》有一个想法