上一篇介绍了虚拟文件系统VFS的基本数据结构,包括:文件系统类型file_system_type、超级块super_block、索引节点inode、目录项dentry和文件对象file。本篇文章着重看一下与进程相关的数据结构,包括files_struct和fs_struct,两者通过task_struct(进程)结构体粘结起来,通过fs_struct可以获取文件系统、挂载点、根dentry等信息,通过files_struct可以打开的文件对象,进而获取目录项、索引节点,最后和物理文件建立联系。
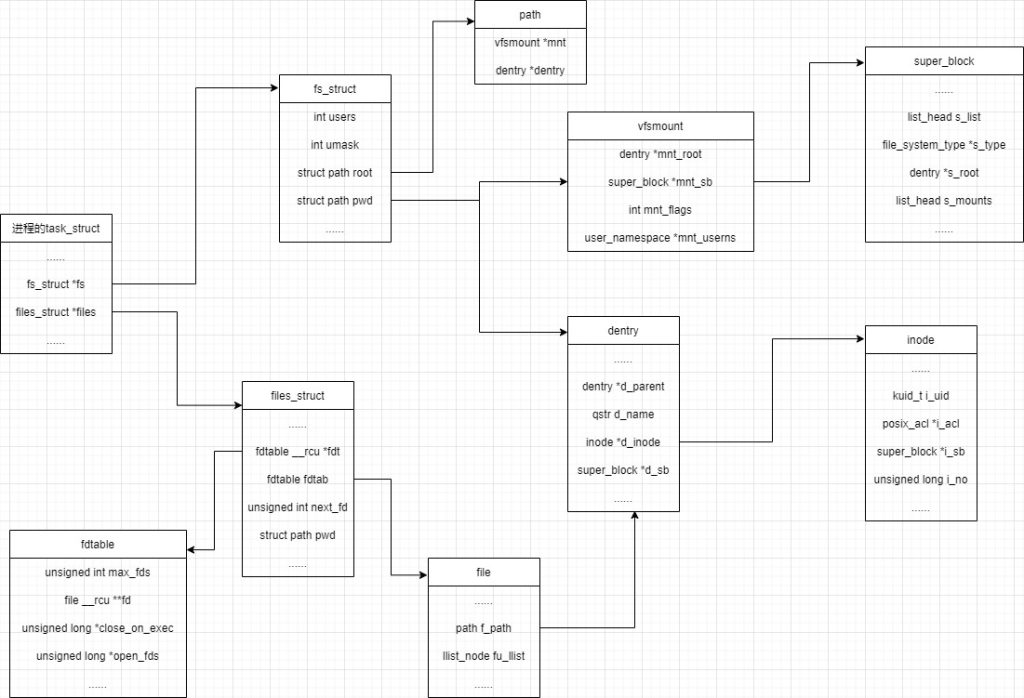
一、主要结构体说明
1.files_struct
进程打开的文件表,用来记录文件描述符的使用情况,文件描述符是用来描述打开的文件。
| 数据结构 | 包含字段 | 结构说明 |
| files_struct | 结构体使用计数atomic_t count 文件描述符表struct fdtable fdtab 1)文件描述符上限max_fds 2)打开的文件描述符open_fds 3)文件对象fd | ftable.h 1)进程通过task_struct中的files域来了解它当前所打开的文件对象; 2)文件对象通过域f_dentry找到它对应的目录项对象,再由目录项对象的d_inode域找到它对应的索引结点,这样就建立了文件对象与实际的物理文件的关联。 |
2.fs_struct
描述进程与文件系统之间的关系,通过此字段可以获取文件系统、挂载信息、根dentry、当前目录dentry信息等
| 数据结构 | 包含字段 | 结构说明 |
| fs_sturct | 自旋锁:spinlock_t lock 自旋锁计数器:seqcount_spinlock_t seq 默认权限:umask 目录项和挂载点信息: 1)根目录 2)当前目录 struct path { struct vfsmount *mnt; struct dentry *dentry; } | fs_struct.h 进程通过task_struct中的fs域(fs_struct结构)了解进程所在的文件系统、挂载信息、根dentry、当前目录dentry信息等 |
二、详细数据结构
// fdtable.h
/*
* Open file table structure
*/
struct files_struct {
/*
* read mostly part
*/
atomic_t count;
bool resize_in_progress;
wait_queue_head_t resize_wait;
struct fdtable __rcu *fdt;
struct fdtable fdtab;
/*
* written part on a separate cache line in SMP
*/
spinlock_t file_lock ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
unsigned int next_fd;
unsigned long close_on_exec_init[1];
unsigned long open_fds_init[1];
unsigned long full_fds_bits_init[1];
struct file __rcu * fd_array[NR_OPEN_DEFAULT];
};
struct fdtable {
unsigned int max_fds;
struct file __rcu **fd; /* current fd array */
unsigned long *close_on_exec;
unsigned long *open_fds;
unsigned long *full_fds_bits;
struct rcu_head rcu;
};// fs_struct.h
struct fs_struct {
int users;
spinlock_t lock;
seqcount_spinlock_t seq;
int umask;
int in_exec;
struct path root, pwd;
} __randomize_layout;
struct path {
struct vfsmount *mnt;
struct dentry *dentry;
} __randomize_layout;上一篇:虚拟文件系统VFS基本数据结构
参考资料:

《004 虚拟文件系统VFS与进程相关的数据结构》有2个想法