上一篇讲了超级块,超级块存储了文件系统的基础信息,以及文件系统的控制信息。而今天介绍的索引节点数据结构,负责保存文件系统中实际文件一般信息,文件系统使用inode管理文件和目录。与超级块类似,索引节点也有三种形态:
- 持久化的索引节点
- 内存中构建的索引节点
- VFS提取的索引节点公共信息,构建出来的索引节点对象
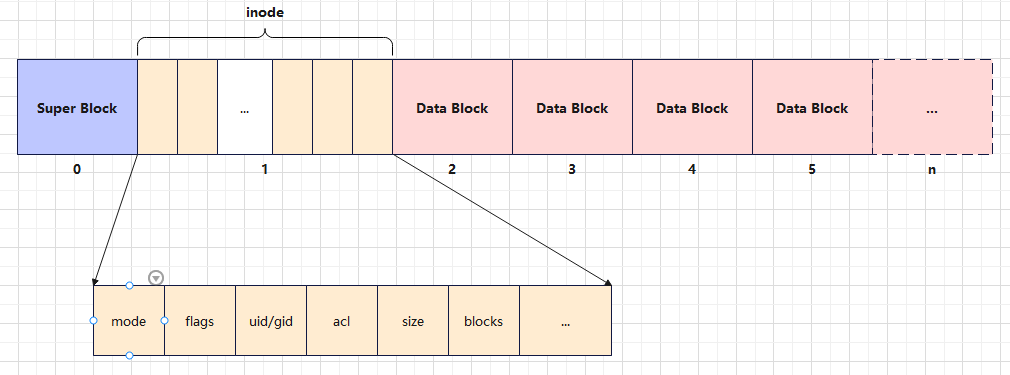
一、文件系统索引节点说明
以下以ext4为例,展示3种形态的索引节点信息。
1. 持久化的索引节点
ext4_inode位于fs/ext4/ext4/h头文件中,表示持久化到盘上的索引节点结构:
1)其中i_mode表示文件类型
S_ISLNK //是否软链
S_ISREG // 是否常规文件
S_ISDIR // 是否目录
S_ISCHR // 是否字符设备
S_ISBLK // 是否块设备
S_ISFIFO // 是否FIFO涉笔
S_ISSOCK // 是否块套接字设备
2)块数量:i_blocks_lo,ext4文件系统默认块大小为4K
3)字段i_block存储数据块信息,这个数组长度是一个宏,宏定义如下,按照宏来看长度是15,为啥是15?这个字段在ext2/ext3和ext4两个版本中差异比较大,其中ext2/ext3采用直接+间接寻址方式,而ext4采用Extent B+树的方式,后面的章节会详细讲解。
#define EXT4_N_BLOCKS (EXT4_TIND_BLOCK + 1)
/*
* Structure of an inode on the disk
*/
struct ext4_inode {
__le16 i_mode; /* File mode */
__le16 i_uid; /* Low 16 bits of Owner Uid */
__le32 i_size_lo; /* Size in bytes */
__le32 i_atime; /* Access time */
__le32 i_ctime; /* Inode Change time */
__le32 i_mtime; /* Modification time */
__le32 i_dtime; /* Deletion Time */
__le16 i_gid; /* Low 16 bits of Group Id */
__le16 i_links_count; /* Links count */
__le32 i_blocks_lo; /* Blocks count */
__le32 i_flags; /* File flags */
union {
struct {
__le32 l_i_version;
} linux1;
struct {
__u32 h_i_translator;
} hurd1;
struct {
__u32 m_i_reserved1;
} masix1;
} osd1; /* OS dependent 1 */
__le32 i_block[EXT4_N_BLOCKS];/* Pointers to blocks */
__le32 i_generation; /* File version (for NFS) */
__le32 i_file_acl_lo; /* File ACL */
__le32 i_size_high;
__le32 i_obso_faddr; /* Obsoleted fragment address */
union {
struct {
__le16 l_i_blocks_high; /* were l_i_reserved1 */
__le16 l_i_file_acl_high;
__le16 l_i_uid_high; /* these 2 fields */
__le16 l_i_gid_high; /* were reserved2[0] */
__le16 l_i_checksum_lo;/* crc32c(uuid+inum+inode) LE */
__le16 l_i_reserved;
} linux2;
struct {
__le16 h_i_reserved1; /* Obsoleted fragment number/size which are removed in ext4 */
__u16 h_i_mode_high;
__u16 h_i_uid_high;
__u16 h_i_gid_high;
__u32 h_i_author;
} hurd2;
struct {
__le16 h_i_reserved1; /* Obsoleted fragment number/size which are removed in ext4 */
__le16 m_i_file_acl_high;
__u32 m_i_reserved2[2];
} masix2;
} osd2; /* OS dependent 2 */
__le16 i_extra_isize;
__le16 i_checksum_hi; /* crc32c(uuid+inum+inode) BE */
__le32 i_ctime_extra; /* extra Change time (nsec << 2 | epoch) */
__le32 i_mtime_extra; /* extra Modification time(nsec << 2 | epoch) */
__le32 i_atime_extra; /* extra Access time (nsec << 2 | epoch) */
__le32 i_crtime; /* File Creation time */
__le32 i_crtime_extra; /* extra FileCreationtime (nsec << 2 | epoch) */
__le32 i_version_hi; /* high 32 bits for 64-bit version */
__le32 i_projid; /* Project ID */
};2. 内存中的索引节点
ext4_inode_info结构体是内存中的索引节点,挂载ext4文件系统时,将会在内存中构建此结构。
1)i_data是块信息结构,与持久化的ext4_inode结构体中的i_block对应,一共60个字节,存储Extent信息。
2)i_disksize表示盘上的inode大小
3)vfs_inode指向VFS的索引节点对象
/*
* fourth extended file system inode data in memory
*/
struct ext4_inode_info {
__le32 i_data[15]; /* unconverted */
__u32 i_dtime;
ext4_fsblk_t i_file_acl;
/*
* i_block_group is the number of the block group which contains
* this file's inode. Constant across the lifetime of the inode,
* it is used for making block allocation decisions - we try to
* place a file's data blocks near its inode block, and new inodes
* near to their parent directory's inode.
*/
ext4_group_t i_block_group;
ext4_lblk_t i_dir_start_lookup;
#if (BITS_PER_LONG < 64)
unsigned long i_state_flags; /* Dynamic state flags */
#endif
unsigned long i_flags;
/*
* Extended attributes can be read independently of the main file
* data. Taking i_mutex even when reading would cause contention
* between readers of EAs and writers of regular file data, so
* instead we synchronize on xattr_sem when reading or changing
* EAs.
*/
struct rw_semaphore xattr_sem;
/*
* Inodes with EXT4_STATE_ORPHAN_FILE use i_orphan_idx. Otherwise
* i_orphan is used.
*/
union {
struct list_head i_orphan; /* unlinked but open inodes */
unsigned int i_orphan_idx; /* Index in orphan file */
};
/* Fast commit related info */
struct list_head i_fc_list; /*
* inodes that need fast commit
* protected by sbi->s_fc_lock.
*/
/* Start of lblk range that needs to be committed in this fast commit */
ext4_lblk_t i_fc_lblk_start;
/* End of lblk range that needs to be committed in this fast commit */
ext4_lblk_t i_fc_lblk_len;
/* Number of ongoing updates on this inode */
atomic_t i_fc_updates;
/* Fast commit wait queue for this inode */
wait_queue_head_t i_fc_wait;
/* Protect concurrent accesses on i_fc_lblk_start, i_fc_lblk_len */
struct mutex i_fc_lock;
/*
* i_disksize keeps track of what the inode size is ON DISK, not
* in memory. During truncate, i_size is set to the new size by
* the VFS prior to calling ext4_truncate(), but the filesystem won't
* set i_disksize to 0 until the truncate is actually under way.
*
* The intent is that i_disksize always represents the blocks which
* are used by this file. This allows recovery to restart truncate
* on orphans if we crash during truncate. We actually write i_disksize
* into the on-disk inode when writing inodes out, instead of i_size.
*
* The only time when i_disksize and i_size may be different is when
* a truncate is in progress. The only things which change i_disksize
* are ext4_get_block (growth) and ext4_truncate (shrinkth).
*/
loff_t i_disksize;
/*
* i_data_sem is for serialising ext4_truncate() against
* ext4_getblock(). In the 2.4 ext2 design, great chunks of inode's
* data tree are chopped off during truncate. We can't do that in
* ext4 because whenever we perform intermediate commits during
* truncate, the inode and all the metadata blocks *must* be in a
* consistent state which allows truncation of the orphans to restart
* during recovery. Hence we must fix the get_block-vs-truncate race
* by other means, so we have i_data_sem.
*/
struct rw_semaphore i_data_sem;
struct inode vfs_inode;
struct jbd2_inode *jinode;
spinlock_t i_raw_lock; /* protects updates to the raw inode */
/*
* File creation time. Its function is same as that of
* struct timespec64 i_{a,c,m}time in the generic inode.
*/
struct timespec64 i_crtime;
/* mballoc */
atomic_t i_prealloc_active;
struct list_head i_prealloc_list;
spinlock_t i_prealloc_lock;
/* extents status tree */
struct ext4_es_tree i_es_tree;
rwlock_t i_es_lock;
struct list_head i_es_list;
unsigned int i_es_all_nr; /* protected by i_es_lock */
unsigned int i_es_shk_nr; /* protected by i_es_lock */
ext4_lblk_t i_es_shrink_lblk; /* Offset where we start searching for
extents to shrink. Protected by
i_es_lock */
/* ialloc */
ext4_group_t i_last_alloc_group;
/* allocation reservation info for delalloc */
/* In case of bigalloc, this refer to clusters rather than blocks */
unsigned int i_reserved_data_blocks;
/* pending cluster reservations for bigalloc file systems */
struct ext4_pending_tree i_pending_tree;
/* on-disk additional length */
__u16 i_extra_isize;
/* Indicate the inline data space. */
u16 i_inline_off;
u16 i_inline_size;
#ifdef CONFIG_QUOTA
/* quota space reservation, managed internally by quota code */
qsize_t i_reserved_quota;
#endif
/* Lock protecting lists below */
spinlock_t i_completed_io_lock;
/*
* Completed IOs that need unwritten extents handling and have
* transaction reserved
*/
struct list_head i_rsv_conversion_list;
struct work_struct i_rsv_conversion_work;
atomic_t i_unwritten; /* Nr. of inflight conversions pending */
spinlock_t i_block_reservation_lock;
/*
* Transactions that contain inode's metadata needed to complete
* fsync and fdatasync, respectively.
*/
tid_t i_sync_tid;
tid_t i_datasync_tid;
#ifdef CONFIG_QUOTA
struct dquot *i_dquot[MAXQUOTAS];
#endif
/* Precomputed uuid+inum+igen checksum for seeding inode checksums */
__u32 i_csum_seed;
kprojid_t i_projid;
};3.VFS使用的索引节点对象
inode是VFS使用的索引节点对象,这个对象里包含文件的一半信息,还有inode的操作表信息
/*
* Keep mostly read-only and often accessed (especially for
* the RCU path lookup and 'stat' data) fields at the beginning
* of the 'struct inode'
*/
struct inode {
umode_t i_mode;
unsigned short i_opflags;
kuid_t i_uid;
kgid_t i_gid;
unsigned int i_flags;
#ifdef CONFIG_FS_POSIX_ACL
struct posix_acl *i_acl;
struct posix_acl *i_default_acl;
#endif
const struct inode_operations *i_op;
struct super_block *i_sb;
struct address_space *i_mapping;
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
void *i_security;
#endif
/* Stat data, not accessed from path walking */
unsigned long i_ino;
/*
* Filesystems may only read i_nlink directly. They shall use the
* following functions for modification:
*
* (set|clear|inc|drop)_nlink
* inode_(inc|dec)_link_count
*/
union {
const unsigned int i_nlink;
unsigned int __i_nlink;
};
dev_t i_rdev;
loff_t i_size;
struct timespec64 i_atime;
struct timespec64 i_mtime;
struct timespec64 i_ctime;
spinlock_t i_lock; /* i_blocks, i_bytes, maybe i_size */
unsigned short i_bytes;
u8 i_blkbits;
u8 i_write_hint;
blkcnt_t i_blocks;
#ifdef __NEED_I_SIZE_ORDERED
seqcount_t i_size_seqcount;
#endif
/* Misc */
unsigned long i_state;
struct rw_semaphore i_rwsem;
unsigned long dirtied_when; /* jiffies of first dirtying */
unsigned long dirtied_time_when;
struct hlist_node i_hash;
struct list_head i_io_list; /* backing dev IO list */
#ifdef CONFIG_CGROUP_WRITEBACK
struct bdi_writeback *i_wb; /* the associated cgroup wb */
/* foreign inode detection, see wbc_detach_inode() */
int i_wb_frn_winner;
u16 i_wb_frn_avg_time;
u16 i_wb_frn_history;
#endif
struct list_head i_lru; /* inode LRU list */
struct list_head i_sb_list;
struct list_head i_wb_list; /* backing dev writeback list */
union {
struct hlist_head i_dentry;
struct rcu_head i_rcu;
};
atomic64_t i_version;
atomic64_t i_sequence; /* see futex */
atomic_t i_count;
atomic_t i_dio_count;
atomic_t i_writecount;
#if defined(CONFIG_IMA) || defined(CONFIG_FILE_LOCKING)
atomic_t i_readcount; /* struct files open RO */
#endif
union {
const struct file_operations *i_fop; /* former ->i_op->default_file_ops */
void (*free_inode)(struct inode *);
};
struct file_lock_context *i_flctx;
struct address_space i_data;
struct list_head i_devices;
union {
struct pipe_inode_info *i_pipe;
struct cdev *i_cdev;
char *i_link;
unsigned i_dir_seq;
};
__u32 i_generation;
#ifdef CONFIG_FSNOTIFY
__u32 i_fsnotify_mask; /* all events this inode cares about */
struct fsnotify_mark_connector __rcu *i_fsnotify_marks;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_FS_ENCRYPTION
struct fscrypt_info *i_crypt_info;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_FS_VERITY
struct fsverity_info *i_verity_info;
#endif
void *i_private; /* fs or device private pointer */
} __randomize_layout;| 字段 | 字段涵义 | 使用说明 |
| i_mode | inode类型:文件、目录、链接等等 | #define S_ISLNK(m) (((m) & S_IFMT) == S_IFLNK) #define S_ISREG(m) (((m) & S_IFMT) == S_IFREG) #define S_ISDIR(m) (((m) & S_IFMT) == S_IFDIR) … |
| i_opflags | inode操作标志位 | #define IOP_FASTPERM 0x0001 #define IOP_LOOKUP 0x0002 #define IOP_NOFOLLOW 0x0004 #define IOP_XATTR 0x0008 #define IOP_DEFAULT_READLINK 0x0010 |
| i_uid i_gid | 用户Id和组Id | |
| i_flag | inode标志位 | fs.h S_SYNC S_NOATIME S_APPEND S_IMMUTABLE S_DEAD S_NOQUOTA S_DIRSYNC S_NOCMTIME S_SWAPFILE S_PRIVATE S_IMA S_AUTOMOUNT S_NOSEC S_DAX S_ENCRYPTED S_CASEFOLD S_VERITY |
| i_acl i_default_acl | ACL Entry属性 | |
| i_op | 指向inode操作表 | |
| i_sb | 指向所属的超级块 | |
| i_mapping | 磁盘数据以内存页page为单位保存在缓冲区,通过i_mapping实现这种映射关系 | 如果是目录的inode,指向是dentry在缓冲区内存页page |
| i_ino | inode编号 | 每个文件系统实例是唯一的 |
| i_nlink | 硬链接 | |
| i_rdev | 设备文件的设备号 | |
| i_atime i_mtime i_ctime | 时间戳 | |
| i_size | 文件大小 | 如果是目录的话,i_size是一个块大小,也就是默认为1024字节 |
| i_bytes | 以512字节(2^9)的块为单位,文件最后一个块的字节数 | |
| i_blkbits | 以位为单位块大小 | |
| i_blocks | 分配给文件的磁盘块数,文件使用块的数目 | |
| i_state | inode关联的各种状态标志 | I_DIRTY_SYNC I_DIRTY_DATASYNC I_DIRTY_PAGES I_NEW I_WILL_FREE I_FREEING I_CLEAR I_SYNC 参考:fs.h |
| i_rwsem | 读写信号量用于同步对索引节点的访问 | |
| dirtied_when dirtied_time_when | 记录inode首次被标记为脏位的时间 | |
| i_hash | 将当前inode链接到inode哈希表(双向链表) | 表头在inode.c中 hlist_head *inode_hashtable |
| i_io_list | 链接到当前正在进行I/O操作的索引节点列表 | |
| i_lru | 将inode链接到最近最少使用(LRU)列表,用于缓存管理 | 使用LRU(策略来替换最不常用的inode对象,以确保缓存中存储的是最常访问的inode |
| i_sb_list | 链接接到对应超级块的s_inodes域 | 参见:inode.c list_add(&inode->i_sb_list, &inode->i_sb->s_inodes); |
| i_wb_list | 链接到回写列表 | |
| i_dentry | 链接到应用此inode的目录项双链表表头 | |
| i_version | ||
| i_count i_dio_count i_writecount i_readcount | i_count 使用此inode的进程数量 i_dio_count DIO引用数量 i_writecount | |
| i_fop | 链接到文件对象file的操作表 | |
| i_flctx | 指向文件锁上下文链表 | struct file_lock_context { spinlock_t flc_lock; struct list_head flc_flock; struct list_head flc_posix; struct list_head flc_lease; }; |
| i_data | 索引节点数据地址空间的地址空间对象,作为页缓存的中间媒介 | 它用于将文件的数据块映射到磁盘块。每个inode都有一个地址空间。该结构用来建立缓存数据和后备存储器数据之间的映射关系 |
| i_devices | 链接到设备列表 | |
| i_pipe i_bdev i_cdev i_link i_dir_seq | i_pipe 管道设备 i_bdev 块设备 i_cdev 字符设备 i_link 连接设备 i_dir_seq | |
| i_generation | 该inode的生成编号,用于NFS检测过期的文件指针 | |
| i_fsnotify_mask i_fsnotify_marks | ||
| i_crypt_info | 用于存储与文件加密相关的信息 | |
| i_verity_info | 用于存储与文件完整性验证相关的信息 | |
| i_private | 与文件系统特定或设备特定的私有数据与索引节点关联的指针 |
二、索引节点对象操作表
以下是索引节点操作表,
struct inode_operations {
struct dentry * (*lookup) (struct inode *,struct dentry *, unsigned int);
const char * (*get_link) (struct dentry *, struct inode *, struct delayed_call *);
int (*permission) (struct user_namespace *, struct inode *, int);
struct posix_acl * (*get_acl)(struct inode *, int, bool);
int (*readlink) (struct dentry *, char __user *,int);
int (*create) (struct user_namespace *, struct inode *,struct dentry *,
umode_t, bool);
int (*link) (struct dentry *,struct inode *,struct dentry *);
int (*unlink) (struct inode *,struct dentry *);
int (*symlink) (struct user_namespace *, struct inode *,struct dentry *,
const char *);
int (*mkdir) (struct user_namespace *, struct inode *,struct dentry *,
umode_t);
int (*rmdir) (struct inode *,struct dentry *);
int (*mknod) (struct user_namespace *, struct inode *,struct dentry *,
umode_t,dev_t);
int (*rename) (struct user_namespace *, struct inode *, struct dentry *,
struct inode *, struct dentry *, unsigned int);
int (*setattr) (struct user_namespace *, struct dentry *,
struct iattr *);
int (*getattr) (struct user_namespace *, const struct path *,
struct kstat *, u32, unsigned int);
ssize_t (*listxattr) (struct dentry *, char *, size_t);
int (*fiemap)(struct inode *, struct fiemap_extent_info *, u64 start,
u64 len);
int (*update_time)(struct inode *, struct timespec64 *, int);
int (*atomic_open)(struct inode *, struct dentry *,
struct file *, unsigned open_flag,
umode_t create_mode);
int (*tmpfile) (struct user_namespace *, struct inode *,
struct dentry *, umode_t);
int (*set_acl)(struct user_namespace *, struct inode *,
struct posix_acl *, int);
int (*fileattr_set)(struct user_namespace *mnt_userns,
struct dentry *dentry, struct fileattr *fa);
int (*fileattr_get)(struct dentry *dentry, struct fileattr *fa);
} ____cacheline_aligned;| 函数 | 涵义 | 使用说明 |
| lookup() | VFS在父目录里查询inode | |
| get_link() | ||
| permission() | 由VFS调用,检查类POSIX文件系统的访问权限 | |
| get_acl() | 当有系统调用,从扩展属性中获取ACL时,调用此函数 | |
| readlink() | ||
| create() | 当有系统调用open(2) 和creat(2)时,调用此函数 | 创建文件 |
| link() | 当有系统调用link(2)时,调用此函数 | 创建硬链接 |
| unlink() | 当有系统调用unlink(2)时,调用此函数 | 删除inode,也就是删除文件 |
| symlink() | 当有系统调用symlink(2)时,调用此函数 | 创建符号链接,软连接 |
| mkdir() | 当有系统调用mkdir(2)时,调用此函数 | 创建子目录 |
| rmdir() | 当有系统调用rmdir(2)时,调用此函数 | 删除子目录 |
| mknod() | 当有系统调用mknod(2)时,调用此函数 | 创建设备(char、block)inode或命名管道(FIFO)或套接字 |
| rename() | 当有系统调用rename(2)时,调用此函数 | |
| setattr() | 当有系统调用设置扩展属性时,调用此函数 | |
| getattr() | 当有系统调用获取扩展属性时,调用此函数 | |
| listxattr() | 当有系统调用获取扩展属性时,调用此函数 | |
| update_time() | VFS调用更新指定时间或者i_version信息 | |
| atomic_open() | ||
| tmpfile() | 创建一个临时文件时,调用此函数 | |
| set_acl() | 当有系统调用,设置ACL到扩展属性,调用此函数 | |
| fileattr_set() | 当调用ioctl(FS_IOC_GETFLAGS)和ioctl(FS _IOC_FSGETXATTR)来检索各种文件标志和属性 | |
| fileattr_get() | 调用ioctl(FS_IOC_SETFLAGS)和ioctl(FS _IOC_FSSETXATTR)来更改其他文件标志和属性 |
上一篇:Linux文件系统数据结构详解:超级块super_block
官方文档:文件系统

《007 Linux文件系统数据结构详解:索引节点inode》有2个想法